AI Assignment
We were tasked to add AI to pre-made environments
- > Artificial Life
- > Decision Theory
- > Neural Network
- > Evolutionary Algorithms
Learn More
Project Overview
For my Level 6 Ai Assignment we we're given 4 different applications and tasked to implement different AIs into each of the applications.
- > Artificial Life - A simulation of how fish flock with each other and how a shark would disperse a flock.
- > Decision Theory - Create a chess AI which would make intelligent moves and not blunder pieces - MinMax Algorithms
- > Neural Network - Create a Neural Network to play "Flappy Bird"
- > Evolutionary Algorithms - Create a genetic algorithm to play a tower defense game.
Artificial Life
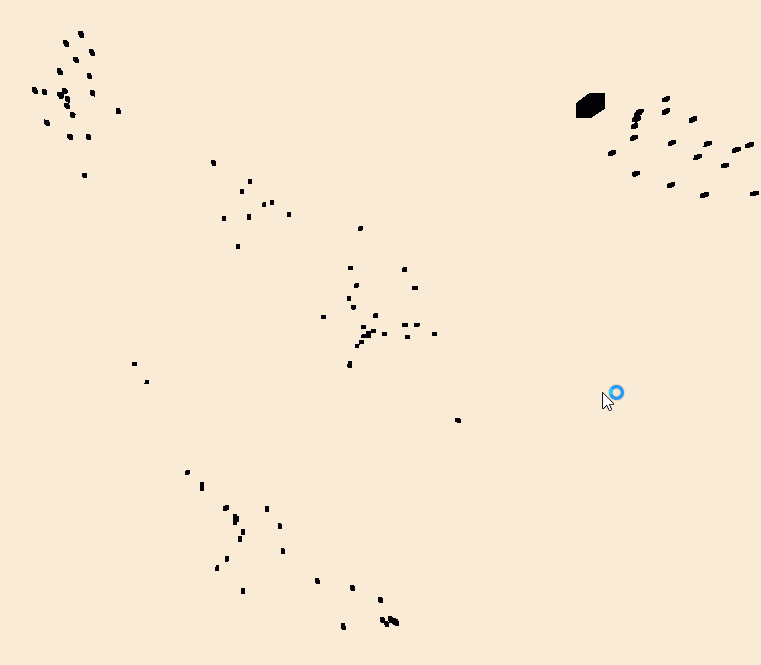
Artificial Life was a project where we were tasked to simulate a fish school and how they would act and respond to predators.
To do this I used steering methods to simulate the different behaviors of the fish and shark
Fish would utilise flocking and flee steering methods as in real life fish seek safety in numbers and they will flee when a shark
is detected as they value their lives over staying as a school.
Sharks on the other hand will actively seek and pursue these fish as they need to eat them to survive.
We can see in the screenshot on the left that the fish are flocking together using Craig Reynolds rules of Alignment, Cohesion, and Separation.
void Boid::Flock(vecBoid nearBoids)
{
// Only run if there are fish to flock with
if (nearBoids.size() > 0)
{
// alignment - allign the fish with the average direction of other fish
XMFLOAT3 alignment = calculateAlignmentVector(&nearBoids);
// Cohesion - move the fish to the average position of the fish
XMFLOAT3 cohesion = calculateCohesionVector(&nearBoids);
// Separation - separate the fish from one another
XMFLOAT3 separation = calculateSeparationVector(&nearBoids);
// Apply the weightings
alignment = multiplyFloat3(alignment, ALIGNMENT_WEIGHT);
cohesion = multiplyFloat3(cohesion, COHESION_WEIGHT);
separation = multiplyFloat3(separation, SEPARATION_WEIGHT);
// Apply the forces
m_direction = addFloat3(m_direction, alignment);
m_direction = addFloat3(m_direction, cohesion);
m_direction = addFloat3(m_direction, separation);
}
}
void Boid::Seek(vecBoid nearBoids)
{
// Only Seek if there are boids nearby
if (nearBoids.size() > 0)
{
// Return Value
XMFLOAT3 desiredLocation = XMFLOAT3(0, 0, 0);
// Set values for the nearest fish to reduce errors
Boid* currentClosestFish = nearBoids[0];
float currentClosestFishDistance = SHARK_VISION_DISTANCE;
for (Boid* boid : nearBoids)
{
XMFLOAT3 otherPos = *boid->getPosition();
// Work out the distance between the boid
float distance = sqrt(((m_position.x - otherPos.x) * (m_position.x - otherPos.x))
+ ((m_position.y - otherPos.y) * (m_position.y - otherPos.y)));
// Compare it with the current closest boid
if (distance < currentClosestFishDistance)
{
// If its closer make it the new closes boid
currentClosestFish = boid;
currentClosestFishDistance = distance;
}
}
// Set the desired location to the closest boids postion
desiredLocation = subtractFloat3(*currentClosestFish->getPosition(), m_position);
// set the speed
desiredLocation = setVectorMagnitude(desiredLocation, SHARK_SPEED);
// Steering
desiredLocation = subtractFloat3(desiredLocation, this->m_direction);
// Apply the force
m_direction = addFloat3(m_direction, desiredLocation);
}
}
Decision Theory
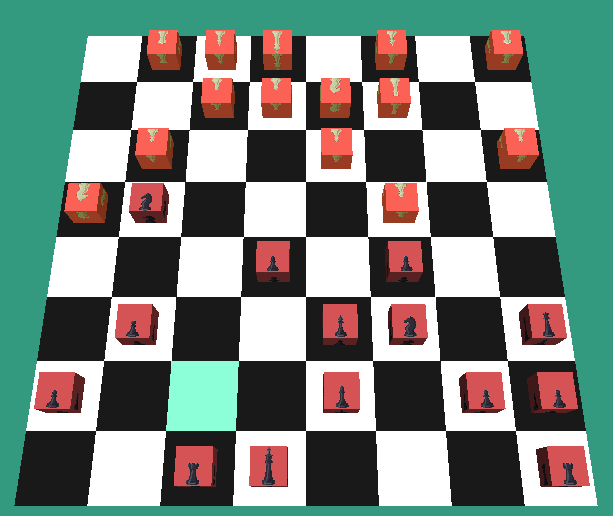
For Decision Theory we were tasked to create a chess ai which would make the best possible moves and prevent blundering.
For example the AI must recognise that taking pieces may not be the best move if it costs them more valuable pieces.
The MiniMax algorithm has been utilised however throughout the project I researched into other algorithms and attempted to implement them
For example the NegaMax algorithm is more suitable in a chess ai as it cuts the codebase down a considerable amount.
To also increase the performance of the algorithm and reduce the overall speed it takes to come to a decision
int ChessPlayer::AlphaBeta(Board* board, int depth, bool maximisingPlayer, int alpha, int beta)
{
if (depth == 0)
{
//cout << "+++++++++++++++++++++" << endl;
//PrintBoard(board);
return EvaluateBoard(board, m_colour);
}
if (maximisingPlayer)
{
int maxEval = -100000000;
vecPieces vPieces;
unsigned int piecesAvailable = getAllLivePiecesOnTeamOnBoard(vPieces, m_colour, board);
// For every valid move
for (int currentPiece = 0; currentPiece < vPieces.size(); currentPiece++)
{
alpha = -100000000;
beta = 100000000;
vector> avaliableMoves = getValidMovesForPiece(board, vPieces[currentPiece]);
for (int currentMove = 0; currentMove < avaliableMoves.size(); currentMove++)
{
// Apply move
int rowStart = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getOriginPosition().first;
int colStart = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getOriginPosition().second;
int rowFin = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getDestinationPosition().first;
int colFin = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getDestinationPosition().second;
std::shared_ptr removedPiece;
if (board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->occupiedState())
{
removedPiece = board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->getOccupyingPiece();
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->removeOccupyingPiece();
}
board->getSquare(rowStart, colStart)->removeOccupyingPiece();
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->occupySquare(vPieces[currentPiece].piece);
int currentEval = AlphaBeta(board, depth - 1, false, alpha, beta);
// Revert move
board->getSquare(rowStart, colStart)->occupySquare(vPieces[currentPiece].piece);
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->removeOccupyingPiece();
if (removedPiece != nullptr)
{
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->occupySquare(removedPiece);
}
//cout << "Piece: " << currentPiece << " Move: " << currentMove << " Score: " << currentEval << endl;
if (currentEval > maxEval)
{
//cout << "Piece: " << currentPiece << " Move: " << currentMove << endl;
maxEval = currentEval;
m_bestMove.move = avaliableMoves[currentMove];
m_bestMoves.clear();
m_bestMoves.push_back(avaliableMoves[currentMove]);
}
if (currentEval == maxEval)
{
m_bestMoves.push_back(avaliableMoves[currentMove]);
}
alpha = max(alpha, maxEval);
if (maxEval > beta)
{
//cout << "Pruned" << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return maxEval;
}
else
{
int minEval = 100000000;
vecPieces vPieces;
unsigned int piecesAvailable = getAllLivePiecesOnTeamOnBoard(vPieces, m_opposingColour, board);
// For every valid move
for (int currentPiece = 0; currentPiece < vPieces.size(); currentPiece++)
{
//cout << "Next piece" << endl;
vector> avaliableMoves = getValidMovesForPiece(board, vPieces[currentPiece]);
for (int currentMove = 0; currentMove < avaliableMoves.size(); currentMove++)
{
// Apply move
int rowStart = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getOriginPosition().first;
int colStart = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getOriginPosition().second;
int rowFin = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getDestinationPosition().first;
int colFin = avaliableMoves[currentMove].get()->getDestinationPosition().second;
std::shared_ptr removedPiece;
if (board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->occupiedState())
{
removedPiece = board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->getOccupyingPiece();
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->removeOccupyingPiece();
}
board->getSquare(rowStart, colStart)->removeOccupyingPiece();
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->occupySquare(vPieces[currentPiece].piece);
int currentEval = AlphaBeta(board, depth - 1, false, alpha, beta);
// Revert move
board->getSquare(rowStart, colStart)->occupySquare(vPieces[currentPiece].piece);
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->removeOccupyingPiece();
if (removedPiece != nullptr)
{
board->getSquare(rowFin, colFin)->occupySquare(removedPiece);
}
if (currentEval < minEval)
{
//cout << "Piece: " << currentPiece << " Move: " << currentMove << endl;
minEval = currentEval;
//m_bestMove.move = avaliableMoves[currentMove];
}
beta = min(beta, minEval);
if (minEval < alpha)
{
//cout << "Pruned" << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return minEval;
}
}
Neural Network
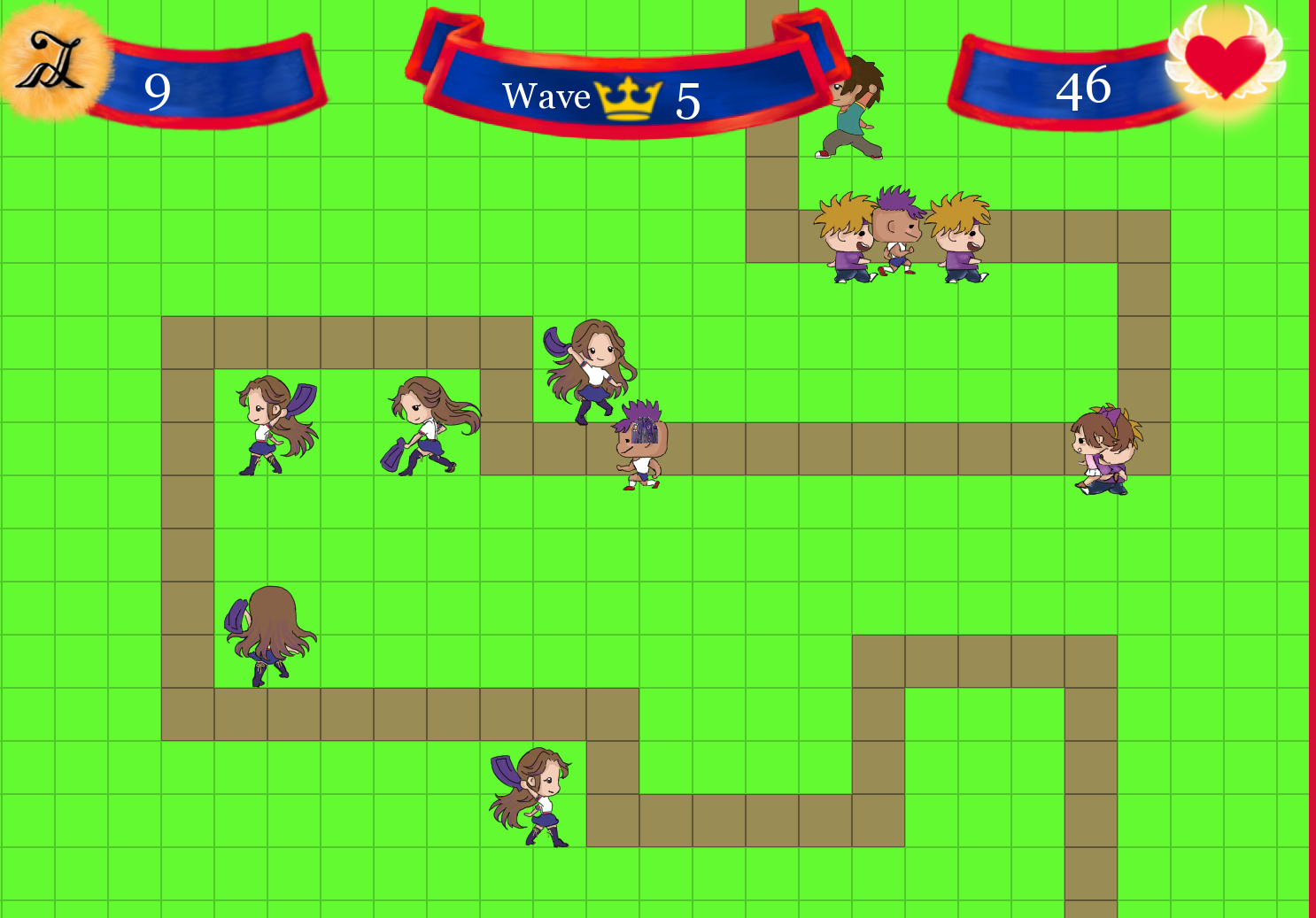
For the neural network project our task was to implement a neural network into flappy bird to allow the birds to complete the game.
However a neural network alone will not allow for any eveolution of the birds and therefore a genetic algorithm has also been used in this application
to allow for the birds to evolve and become better than the last birds.
Since the Genetic Algorithm code is similar to the Evolutionary Algorithm Project I will only include Neural Network Code snippets in this section
I also made a lot of changes to the base game as it only allowed 1 bird and had logic for 1 bird, adding the ability to have more birds on the screen allows
us to see the best birds per generation within real-time and made the application run quicker as whole generations are being played at a time.
The input nodes took in the distance to the center of the gap between the pipes, the distance to the floor, and the distance to the next set of pipes,
the neural network then processes this data and returns one output which is wether the bird should flap or not flap.
bool AIController::NeuralNetworkLogic(Land* land, Bird* bird, Pipe* pipe)
{
// Input nodes
_neuralNetwork[0][0] = distanceToCentreOfPipeGap(pipe, bird);
_neuralNetwork[0][1] = distanceToFloor(land, bird);
_neuralNetwork[0][2] = distanceToNearestPipes(pipe, bird);
for (int i = 0; i < _neuralNetwork.size() - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < _neuralNetwork[i + 1].size(); j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < _neuralNetwork[i].size(); k++)
{
_neuralNetwork[i + 1][j] += _neuralNetwork[i][k] * _NNweights[i][k][j];
}
// activation - hyperbolic tangent
if (0 >= _neuralNetwork[i + 1][j])
{
_neuralNetwork[i + 1][j] = pow(2, _neuralNetwork[i + 1][j]) - 1;
}
else
{
_neuralNetwork[i + 1][j] = 1 - pow(2, -_neuralNetwork[i + 1][j]);
}
}
}
return 0 <= _neuralNetwork[2][0];
} Evolutionary Algorithms
For the Evolutionary Algorithms project our task was to implement a genetic algorithm into the application to achieve a score of 190+ in the game.
The Genetic Algorithms initial population is created through random values and then run, each different solution will have its own fitness and this is what is used
to determine which solutions are chosen within the generation of the next population.
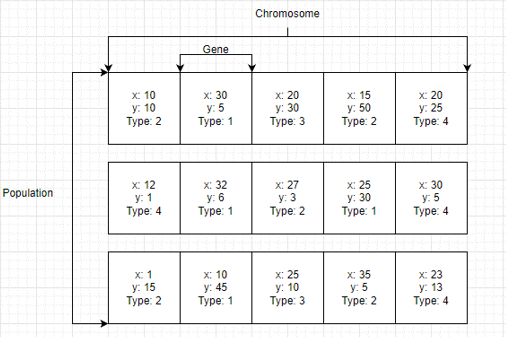
To add some variation to the algorithm to prevent the algorithm converging too quickly I implemented mutation. The mutation is a small chance and it mutates some
of the genes of the chromosome. To show how the genetic algorithm is layed out within my code I created a diagram. One gene is a tower and the information a tower holds,
and a chromosome is a list of these genes to create a final solution
void Population::GenerateNextPopulation()
{
// Firstly lets order the chromosomes based on their performance and give them a rank
SortChromosomes();
m_lastGenerationBest = m_Chromosomes.back();
// Now we should give these chromosomes their ranks
// We are giving them ranks as Ranked selection gives stronger chromosomes than roulettwheel
for (int i = 0; i < m_Chromosomes.size(); i++)
{
m_Chromosomes[i]->SetRank(i + 1);
}
vector nextPopulation;
// Elitism - allows for a stronger next generation
Chromosome* bestChromosome = m_Chromosomes.back();
bestChromosome->SetCurrentGene(0);
bestChromosome->Print();
nextPopulation.push_back(bestChromosome);
// Now we've given them ranks lets do reproduction to create the next population
for (int i = 0; i < m_Chromosomes.size()-1; i += 2)
{
Chromosome* parent1 = RouletteWheelSelection();
Chromosome* parent2 = RouletteWheelSelection();
while (parent1 == parent2)
{
parent2 = RouletteWheelSelection();
}
Chromosome* offspring1 = Reproduce(parent1, parent2);
Chromosome* offspring2 = Reproduce(parent2, parent1);
// now that we have some children lets add some mutation
int mutationRoll1 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, 100);
if (mutationRoll1 <= m_iMutationChance)
{
offspring1 = Mutate(offspring1);
}
nextPopulation.push_back(offspring1);
int mutationRoll2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, 100);
if (mutationRoll2 <= m_iMutationChance)
{
offspring2 = Mutate(offspring2);
}
if (1 != m_Chromosomes.size() -1)
{
nextPopulation.push_back(offspring2);
}
}
//Swap the populations over
m_Chromosomes.clear();
cout << nextPopulation.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < nextPopulation.size(); i++)
{
m_Chromosomes.push_back(nextPopulation[i]);
}
m_iGenerationCount++;
}
Chromosome* Population::Reproduce(Chromosome* parent1, Chromosome* parent2)
{
// time to create a offspring from 2 parents
Chromosome* offspring = new Chromosome();
for (int i = 0; i < parent1->GetGeneCount(); i += 2)
{
offspring->AddGene(parent1->GetGeneAt(i));
// Only add the gene if we have space
if (i != parent1->GetGeneCount() - 1)
{
offspring->AddGene(parent2->GetGeneAt(i+1));
}
}
return offspring;
}
Chromosome* Population::Mutate(Chromosome* c)
{
Chromosome* returnChromosome = new Chromosome();
for (int i = 0; i < c->GetGeneCount(); i++)
{
returnChromosome->AddGene(c->GetGeneAt(i));
}
int mutationTypeRoll = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(1, 5);
if (mutationTypeRoll == 1)
{
cout << "Swap Mutation" << endl;
// Swap mutation
int randomIndex1 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
int randomIndex2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
// make sure indexs are different
while (randomIndex1 == randomIndex2)
{
randomIndex2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
}
cout << randomIndex1 << " " << randomIndex2 << endl;
Gene temp;
temp = returnChromosome->GetGeneAt(randomIndex1);
returnChromosome->SetGeneAt(randomIndex1, returnChromosome->GetGeneAt(randomIndex2));
returnChromosome->SetGeneAt(randomIndex2, temp);
return returnChromosome;
}
else if (mutationTypeRoll == 2)
{
cout << "Reverse Mutation" << endl;
// Reverse Mutation
int randomIndex1 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
int randomIndex2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
// make sure indexs are different
while (randomIndex1 == randomIndex2)
{
randomIndex2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
}
// make sure random number 1 is smaller
if (randomIndex2 < randomIndex1)
{
int temp = randomIndex1;
randomIndex1 = randomIndex2;
randomIndex2 = temp;
}
// Get section to flip
vector selectedGenes;
for (int i = randomIndex1; i < randomIndex2; i++)
{
selectedGenes.push_back(returnChromosome->GetGeneAt(i));
}
// Perform flip
int n = selectedGenes.size() - 1;
for (int i = randomIndex1; i < randomIndex2; i++)
{
returnChromosome->SetGeneAt(i, selectedGenes[n]);
n--;
}
return returnChromosome;
}
else
{
cout << "Reverse Random" << endl;
// Random Mutation
int randomIndex1 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
int randomIndex2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
cout << randomIndex1 << endl;
cout << randomIndex2 << endl;
// make sure indexs are different
while (randomIndex1 == randomIndex2)
{
randomIndex2 = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, c->GetGeneCount() - 1);
}
Gene tp;
tp.x = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, 25);
tp.y = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, 17);
tp.towerType = (TowerType)(AIController::GenerateRandomNum(1, 3));
// Add the gene to the Chromosome
returnChromosome->SetGeneAt(randomIndex1, tp);
tp.x = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, 25);
tp.y = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(0, 17);
tp.towerType = (TowerType)(AIController::GenerateRandomNum(1, 3));
returnChromosome->SetGeneAt(randomIndex2, tp);
return returnChromosome;
}
}
Chromosome* Population::RankSelection()
{
Chromosome* selectedChromosome = new Chromosome();
int maxWheelSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m_Chromosomes.size(); i++)
{
maxWheelSize += m_Chromosomes[i]->GetRank();
}
int selectedNum = AIController::GenerateRandomNum(1, maxWheelSize-1);
int wheelTotal = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m_Chromosomes.size(); i++)
{
wheelTotal += m_Chromosomes[i]->GetRank();
if (wheelTotal > selectedNum)
{
selectedChromosome = m_Chromosomes[i];
break;
}
}
return selectedChromosome;
} I am happy to go into further detail for this or any projects on my portfolio if needs be. I'm unsure of the rights to the games we were given to work on therefore I have not made a public github repo at this time, however if needs be i am more than happy to distribute just my code for the algorithms